
| Interferometry |  |
The processing setup for InSAR is similar like for the other functionalities. The set of interferometric operators is designed and chained into the graph via the Graph Processing Framework (GPF).
For optimal interferometric processing, many of the core functionalities are improved and/or reimplemented to accommodate for the InSAR requirements. Some of the extended modules are , e.g., Warping function extended with phase preserving and more accurate interpolation kernels. While, the coregistration has been fully reimplemented and optimized for interferometric applications.
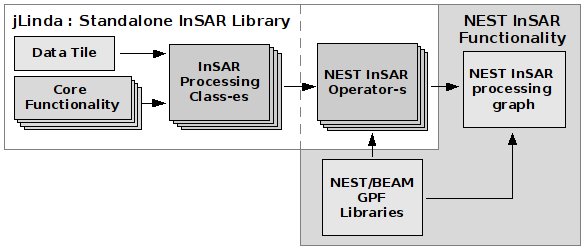
Initially for InSAR functionality, as an algorithmic prototype the DORIS (Delft object-oriented radar interferometric software) software has been used. However, in the course of development many of these algorithmic prototypes have been further extended and completely reimplemented, and most of implementations significantly deviated from the original. Because of these developments, and in order to streamline and simplify further developments a dedicated library and application interface (API) for interferometric application is designed and developed - jLinda (Java Library for Interferometric Data Analysis).
The architecture of interferometric modules are visualized in Figure 1.
All implemented algorithms are fully documented, described in the literature, and follow a generally accepted best practices.