
| Coregistration |  |
The sub-pixel coregistration of SAR images is a strict requirement and critical component of any interferometric processing chain. It is an essential step for the accurate determination of phase difference, and applications such as DEM map generation, interferometric deformation analysis, etc.
The interferometric modules of the toolbox will
accurately co-register one or more secondary images
with respect to a reference image. The co-registration procedure is
completely automatic. Apart from defining the processing
parameters, no additional input nor intervention from the user is
required. For example the distribution of correlation
(optimization) windows are done in automatic manner for both
reference and secondary image. Also, the refinement of the
coregistration offsets is done in a fully automatic way, including
downloading and interpolation of the a-priori
digitial-elevation-model.
The implementation of the coregistration procedure is based on the
cross-correlation technique. Since this technique for an optimal
alignment tend to be slow for very large search windows, the
procedure is usually separated in two main steps: coarse and
fine coregistration. In the coarse coregistration, the
offsets are approximated either by using the satellite orbits and
timing as a reference, and/or by defining an approximate common
points in reference/secondary images and performing correlation
matching with large windows. The subsequent fine coregistration
applies automation correlation technique to obtain sub-pixel
alignment accuracy. After the coregistration offsets are computed,
the estimation of the coregistration polynomial (CPM) and
interferometric resampling of secondary images to the reference
geometry is performed.
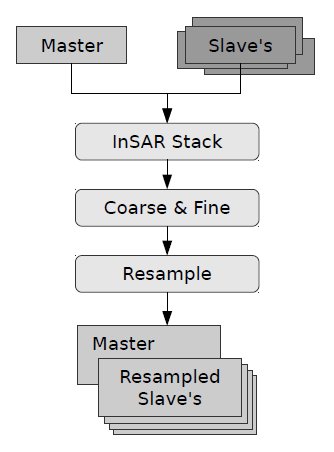
The interferometric coregistration is performed by create stack,
coarse fine coregistration and resampling.
Input SAR images may be fully ("full frame") or only partially
overlapping ("subset"), they have to be from acquisitions taken at
different times using compatible, in the interferometric sense,
sensors, and input images must belong to the same type (i.e., them
must be complex).
While in principle the implementation of the InSAR coregistration
is flexible enough to allow processing of real (detected) products,
for now only complex (single-look-complex) data is supported.
The Create Stack operator collocates the reference and secondary images based into a single reference (reference) geometry. Basically the secondary image data is subset into geometry of the reference image. With performing this operation the reference and secondary images share the same geo-positioning information, and have the similar dimensions. For overlap and geometry calculation either orbital data, or annotated tie-point-grids (i.e., ground-control-points) can be used. In other words the coarse coregistration is performed using orbital information or annotated GCPs. The method based on orbits is recommended for all platforms, since especially in case of old sensors (ERS1/2) annotated GCPs prove not to be reliable through-out the whole mission lifetime.
More details on this operator are given in the operator help - Create Stack.
The Cross Correlation operator creates an alignment between
reference and secondary images by matching automatically
distributed correlation optimization windows to their corresponding
secondary windows. There are two steps: coarse and fine
registration. The offsets between reference and secondary are
computed by maximizing the cross-correlation between reference and
secondary images on a series of imagettes defined across the
images. First on coarse level, with large windows and lower
oversampling factors, later on fine level, with smaller windows and
higher oversampling factors.
For details and specifics on the operators input parameters,
readers are referred to operators help Cross Correlation.
With the reference-secondary offsets computed, a coregistration
polynomial (CPM) is estimated by the Warp operator, which resamples
pixels in the secondary image into pixels in the reference
image.
This resampling is performend in two-steps: (1) reconstruction of
the continuous signal from its sampled version by convolution with
an interpolation kernel, and (2) sampling of the constructed signal
at the new sampling locations.
For details of the Warp operator, readers are referred to Warp operator.
Processing steps that are listed below should give satisfactory
results for most of the interferometric combinations.