Terrain Flattening Operator
When land cover classification is applied to terrain that is not
flat, inaccurate classification result is produced. This is because
that terrain variations affect not only the position of a
target on the Earth's surface, but also the brightness of the radar
return. Without treatment, the radiometric biases caused by terrain
variations are introduced into the coherency and covariance
matrices. It is often seen that the classification result mimic the
radiometry rather than the actual land cover. This operator removes
the radiometric variability associated with topography using the
Radiometric Terrain Correction algorithm proposed by Small [1]
while leaving the radiometric variability associated with land
cover.
In the Radiometric Terrain Correction algorithm [1], the
radiometric effect is simulated using a digital elevation model
(DEM) of the imaged area. It is therefore required that
the DEM resolution must be higher than the image resolution.
In case that the DEM resolution is lower than the image resolution,
users have two options:
- Oversample the DEM to higher resolution, which generally will
lead to longer the processing time and occasional artefacts in the
image;
- Multilook the source image to lower resolution, which will
reduce the processing time and produce generally better
image.
Input and Output
- The input to this operator should be calibrated beta0. For
polarimetric SAR product, it should be in T3, C3, C2 matrix
format.
- The output of this operator is terrain flattened gamma0. For
polarimetric SAR product, the output is terrain flattened coherency
or covariance matrices in T3, C3 or C2 format.
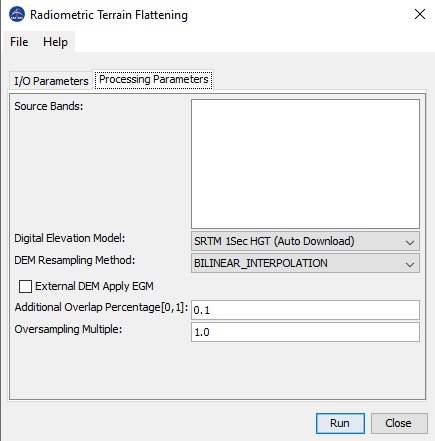
Parameters Used
The following processing parameters are used for this
operator:
- Source Bands: source product bands. User can select one or more
bands for terrain flattening. If no band is selected, by default
all bands are selected for terrain flattening.
- Digital Elevation Model: available digital elevation models
used in computing local illuminated area.
- DEM resampling Method: resampling method used in getting
elevation from DEM.
- External DEM: User specified external DEM file. Currently
only DEM in Geotiff format with geographic coordinates
(Plat, Plon, Ph) referred to
global geodetic ellipsoid reference WGS84 (and height in
meters) is supported.
- DEM No Data Value: No Data Value for user specified external
DEM.
- External DEM Apply EGM: checkbox if selected, Earth Gravitional
Model will be applied to the user specified external
DEM.
- Additional Overlap Percentage: To perform terrain flattening to
a given tile, pixels from adjacent tiles are generally needed due
to the topography in the image area. The overlap percentage is
automatically computed using the DEM. However, if the computed
overlap is not enough, then tiling effect can be observed in the
terrain flattened image. In this case, user can increase the
Additional Overlap Percentage to increase the overlap between
adjacent tiles.
- Oversampling Multiple: The Terrain Flattening algorithm
requires that the DEM resolution is higher than the image
resolution. Therefore, the DEM is generally oversampled. The
default oversampling factor is automatically computed based on the
DEM resolution and image pixel spacings. The final oversampling
factor = (default oversampling factor) x (Oversampling Multiple).
The default value for Oversampling Multiple is 1.0.
However, if the oversampling factor is not large enough, then
artefacts can be observed in the terrain flattened image. In this
case user can increase the oversampling factor by setting
Oversampling Multiple to a larger value.
Reference:
[1] David Small, "Flattening Gamma: Radiometric Terrain
Correction for SAR imagery", IEEE Transaction on Geoscience and
Remote Sensing, Vol. 48, No. 8, August 2011


