Slant Range to Ground Range Operator
The operator re-projects images from slant
range (range spacing proportional to echo delay) to ground range
(range spacing proportional to distance from nadir along a
predetermined ellipsoid). The operator works on complex or real
slant range product.
Note: The SRGR operator is not required before terrain
correcting since terrain corrected results are always in ground
range.
Major Processing Steps
The slant range to ground range conversion
consists of the following major steps:
- Create a warp polynomial of given order that maps ground range
pixels to slant range pixels.
- For each ground range pixel, compute its corresponding pixel
position in the slant range image using warp polynomial.
- Compute pixel value using user selected interpolation
method.
Interpolation Methods Supported
The operator supports the following interpolation
methods:
- Nearest-Neighbour interpolation
- linear interpolation
- Cubic interpolation
- Cubic2 interpolation
- Sinc interpolation
Parameters Used
The following parameters are used by the
operator:
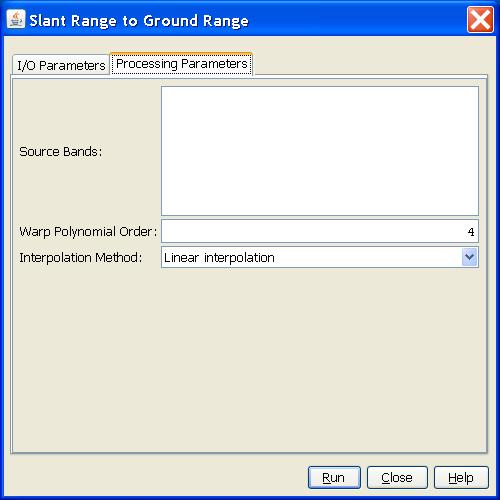
- Source Band: All bands (real or virtual) of the source product.
User can select one or more bands for producing ground range
images. If no bands are selected, then by default all bands are
selected.
- Warp Polynomial Order: The degree of WARP polynomial. It should
be a positive integer.
- Interpolation Method: User can select interpolation method used
in SRGR conversion.